Territory:

Supplies most of medial surface of cerebral cortex (anterior 3/4), frontal pole and anterior portions of corpus callosum.
Perforating branches supply anterior limb of the internal capsule, inferior portions of caudate head and anterior globus pallidus.
Infarction will potentially cause (mainly) lower limb weakness, incontinence, abulia/motor aphasia, frontal lobe symptoms.
Origin
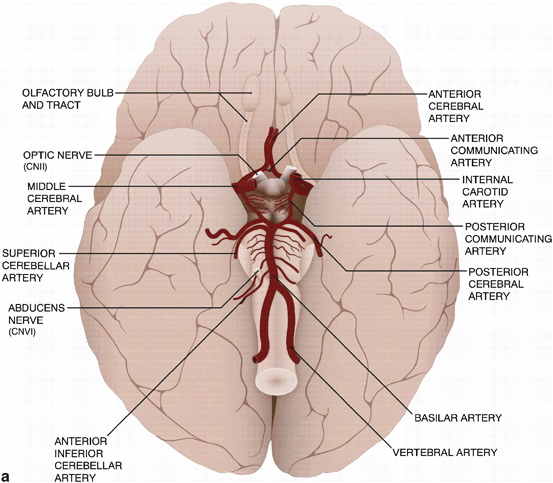
Segments

A1: ICA bifurcation to Acomm (horizontal)
A2: Acomm to origin of CMA around rostrum/genu junction (vertical)
A3: Genu to body of CC (proximal pericallosal)
A4/A5: Continuation of distal pericallosal (directly posterior)
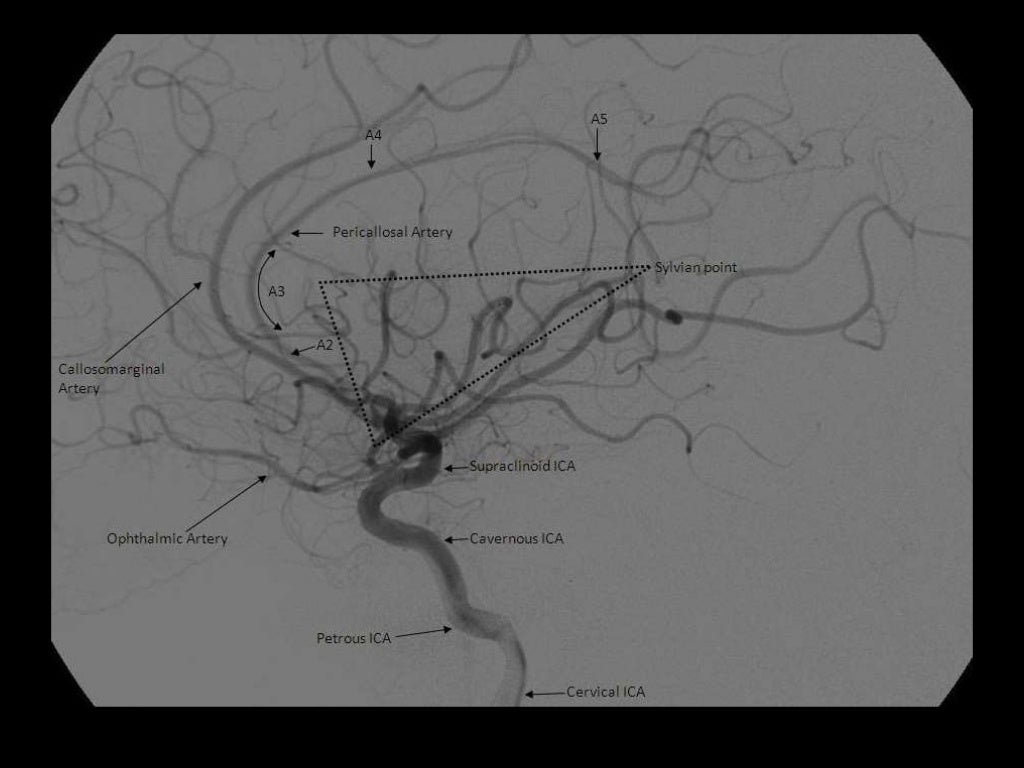
NB angiographic sylvian point = apex of fissure sf. skull sylvian point a surface marking for fissure 3cm behind superior portion of zygomatic process

Branches
A1
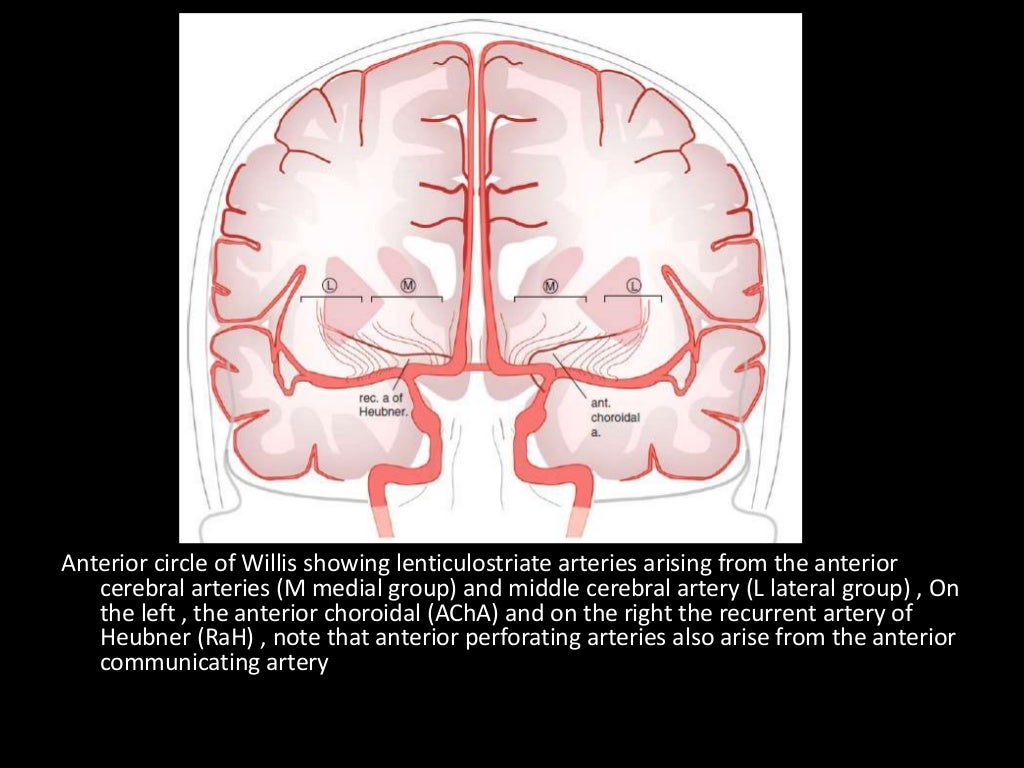
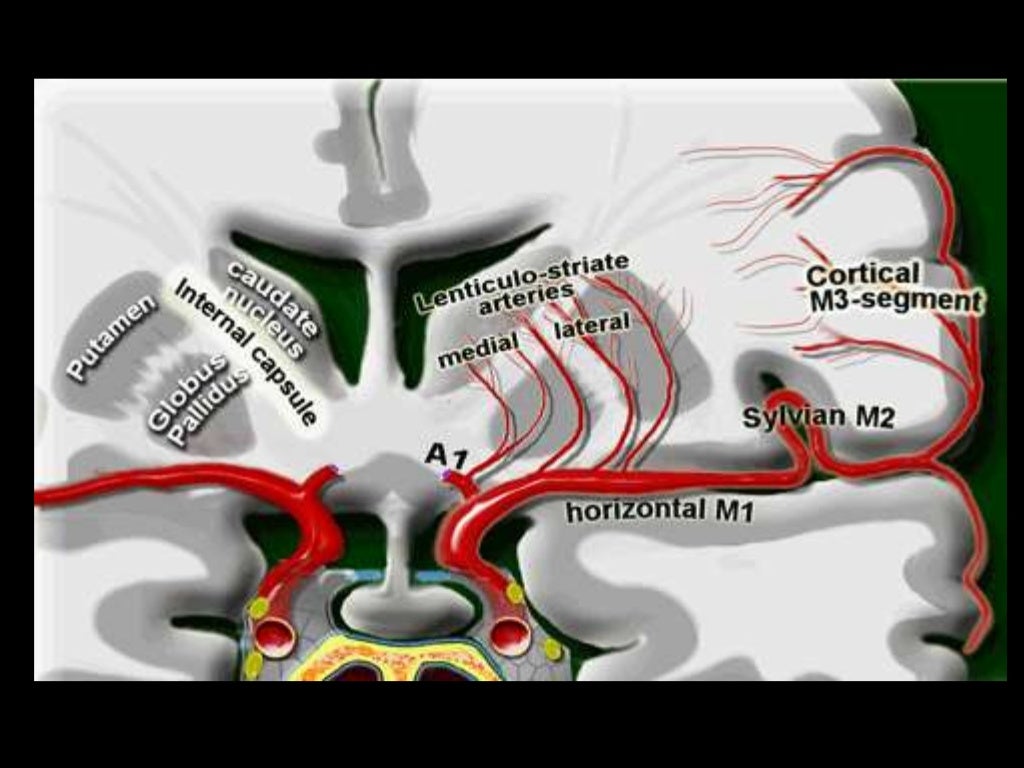
Medial lenticulostriate A.
AComm A.
A2
Recurrent artery of Hubner (= medial striate A.). Supplies head of caudate and anterior limb of IC. (Can be A1 branch)
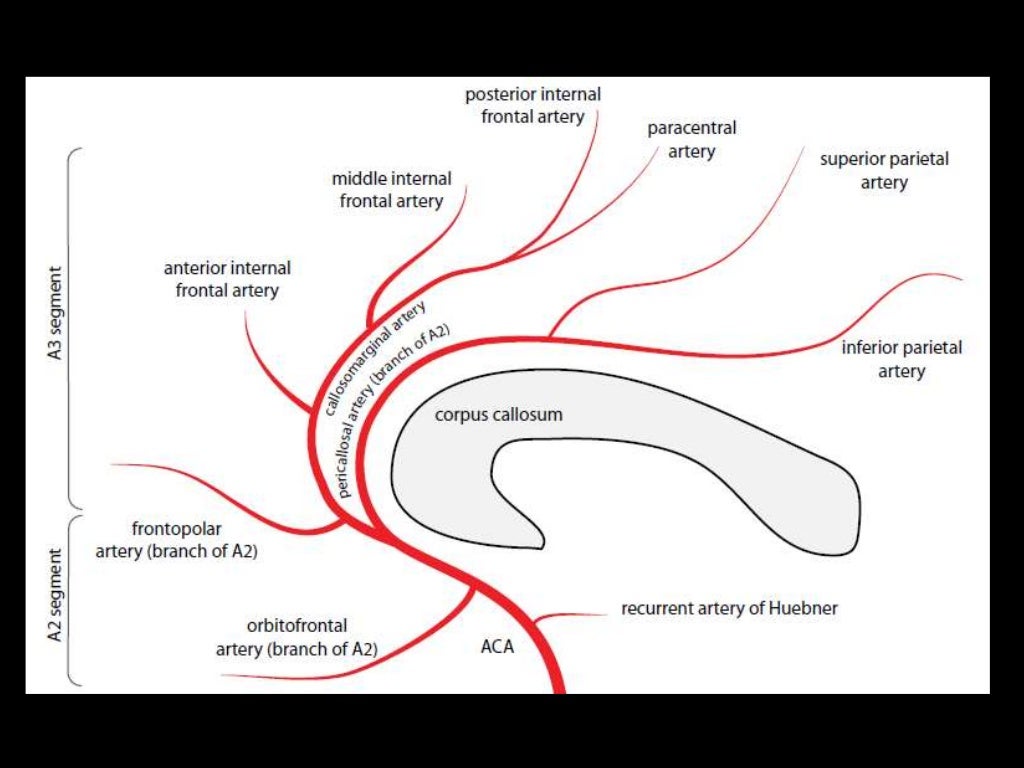
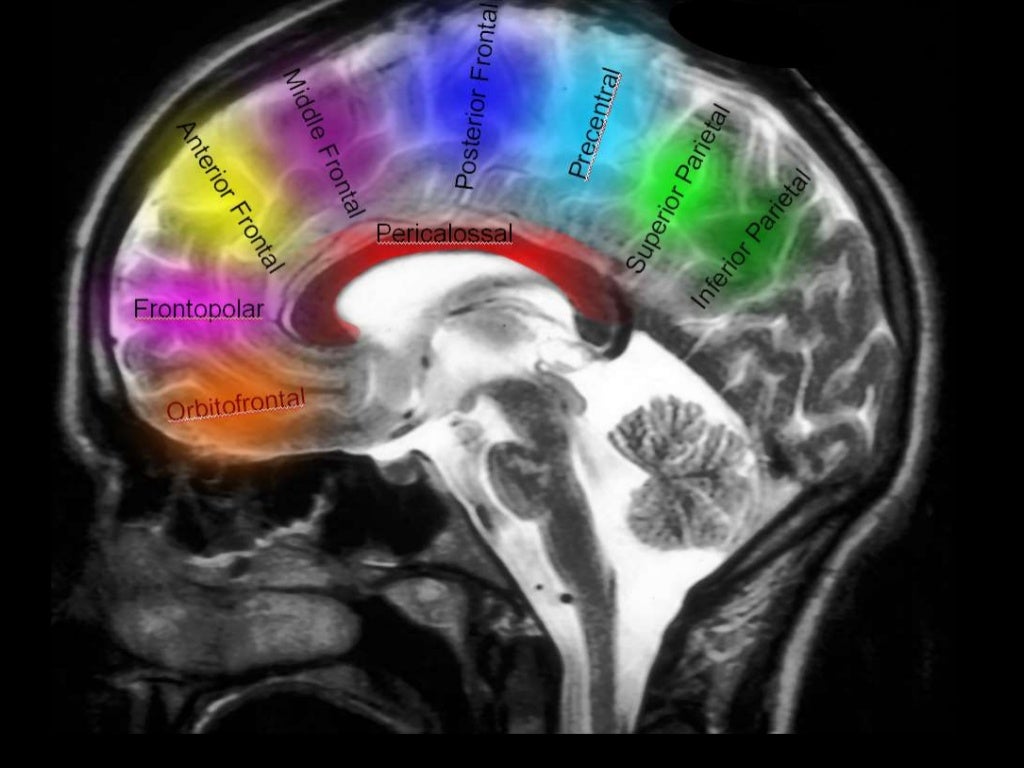
Orbitofrontal A.
Frontopolar A.
A3
Callosomarginal A. (in cingulate sulcus)
Pericallosal A.
Anterior (internal) frontal A.
Middle (internal) frontal A.
Posterior (internal) frontal A.
Paracentral A.
NB Striatum = Caudate + IC + lentiform nucleus (which = putamen + GP).
No comments:
Post a Comment