1. Surface anatomy
Taylor-Haughton Lines
 |
| EAM just behind condylar process of mandible Sylvian Fissure line starts at orbitotemporal angle- where the eyebrow ends. |
- The superior aspect of the motor cortex is almost straight up from the EAM near midline.
- 4-5cm posterior to coronal suture in adults.
- Or 2cm behind midpoint of nasion to inion.
2. Radiological anatomy

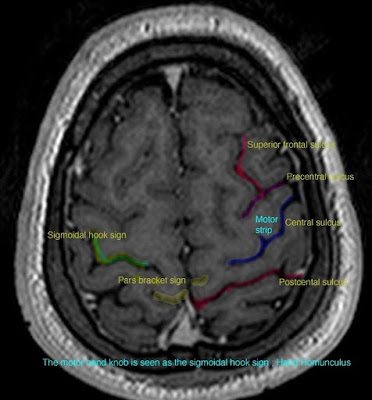
The hand knob representing the hand motor area is in the pre-central gyrus. Looks like upside down omega. Delineates motor strip.


The thickness sign is simply that pre-central sulcus is thicker than post central- usually by 1.5:1.
The postcentral sulcus is also usually bifid.
The L sign- the superior frontal sulcus and precentral sulcus form an L shape. (See image at bottom)
The IFG demonstrates an M shape - this is useful for Broca's area. It also follows that the pre-central gyrus is behind this.
The hook sign represents the hand knob in sagittal plane and so indicates the motor strip.
The pars marginalis sign follow the cingulate sulcus in midline sagittal view. The marginal sulcus (PM) is an extension of this. The post-central gyrus is in front of it.

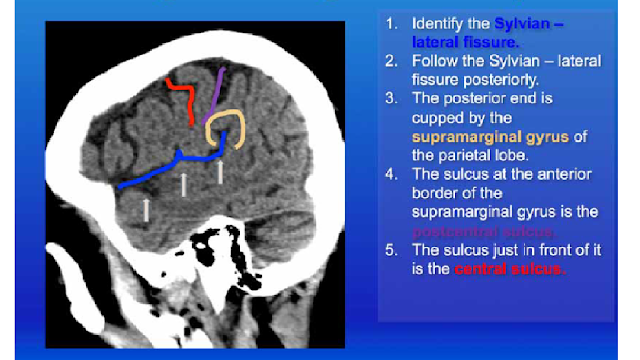
This is easy to use. Central sulcus is in red. Use it!