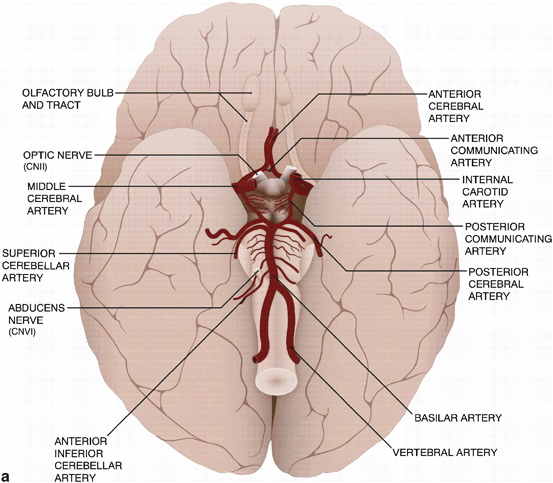
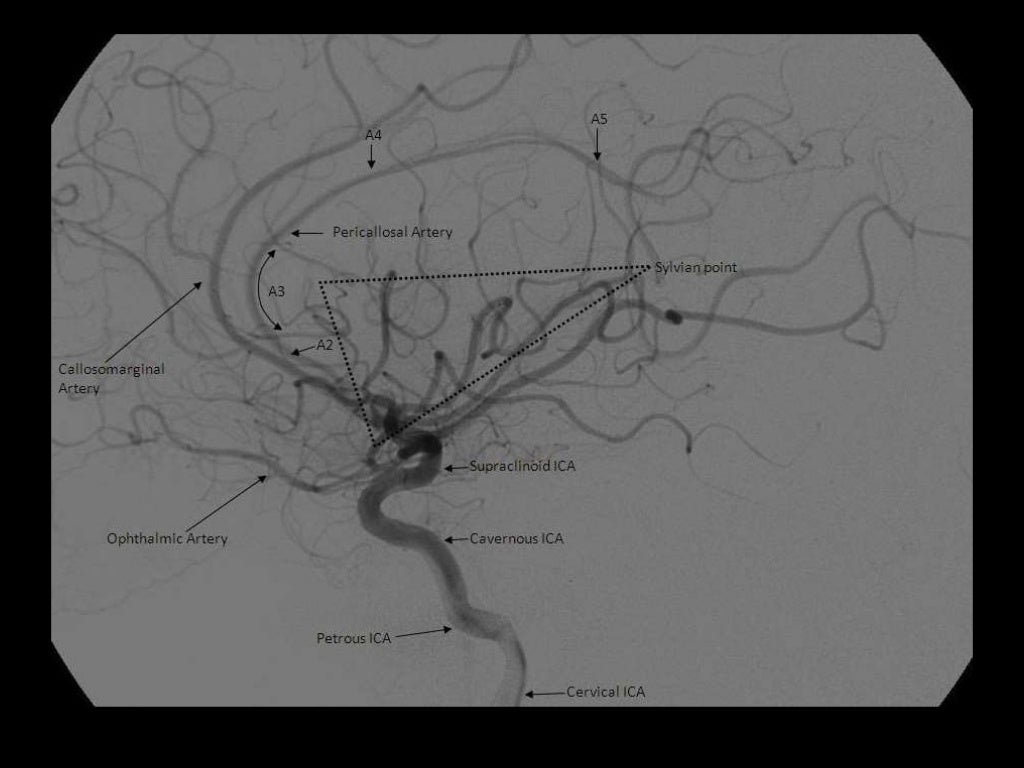
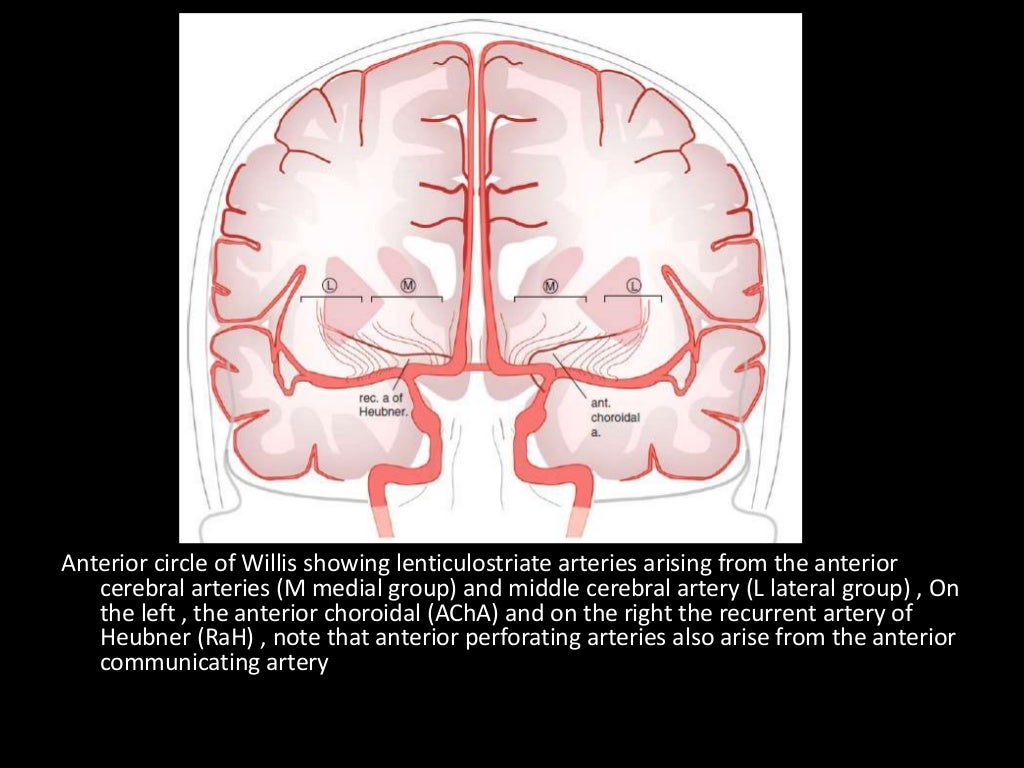
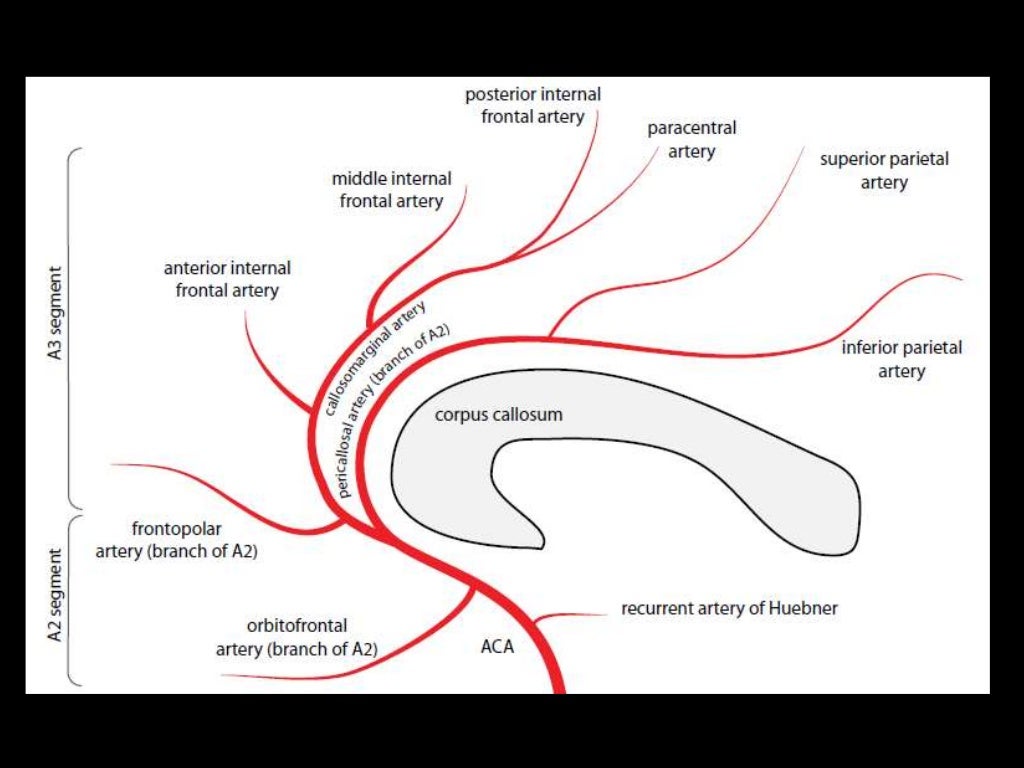
Middle Cerebral Artery:
Territory:

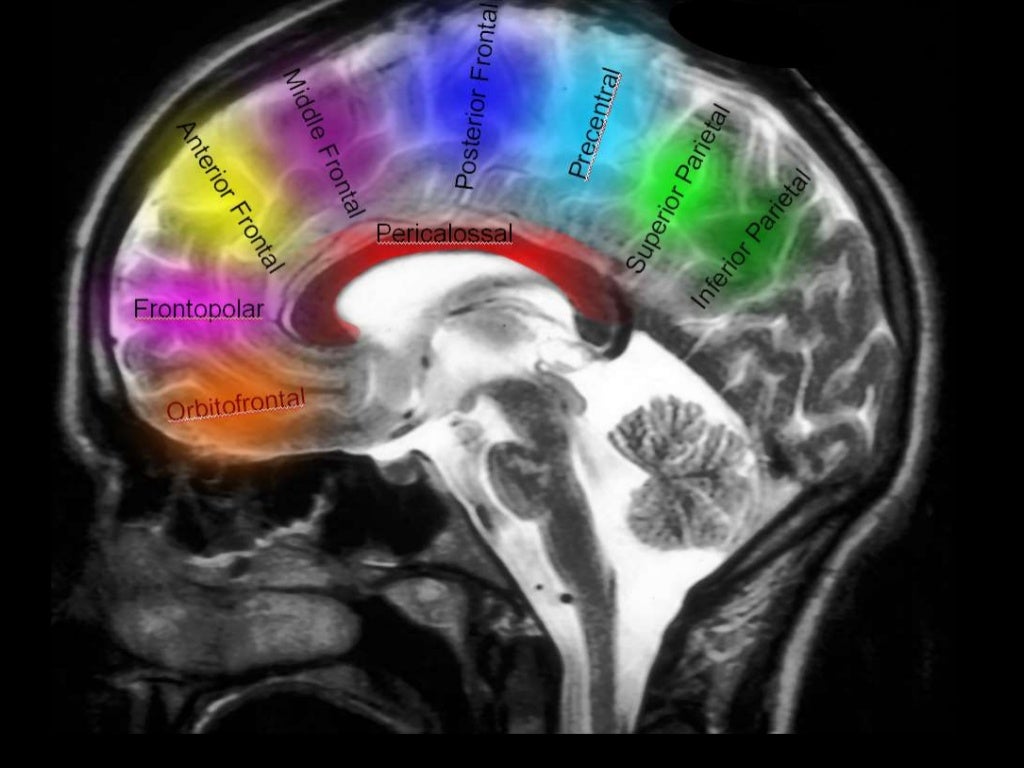
Supplies most of lateral surface of hemisphere, part of internal capsule (posterior part of anterior limb and anterior part of posterior limb) and basal ganglia.
Origin:
Segments:
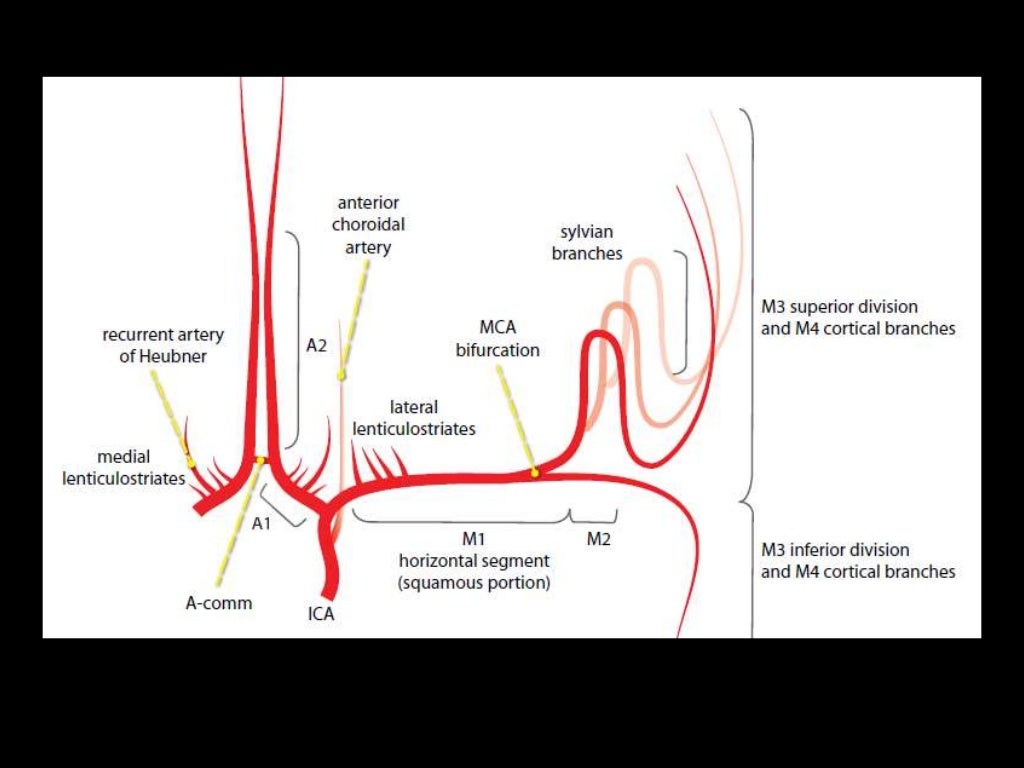
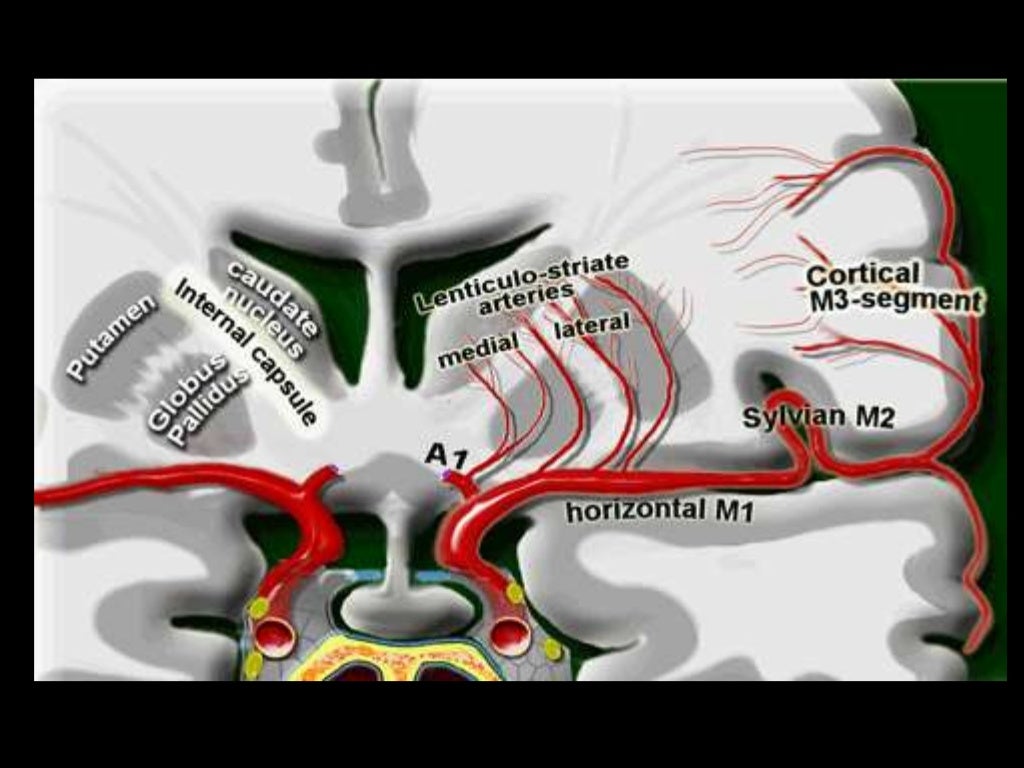
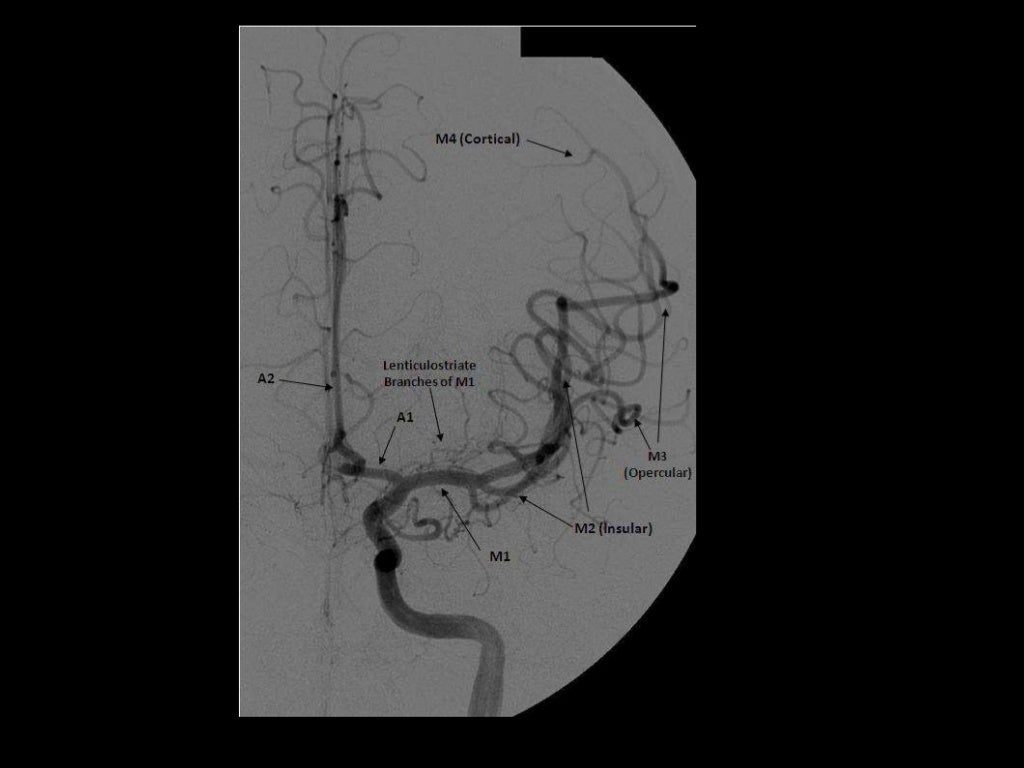
M1- ICA to Sylvian fissure (horizontal or Sphenoidal)
M2- Sylvian (within fissure; also Insular) post bifurcation into superior & inferior divisions.
M3- Opercular: Top of fissure to cerebral cortex
M4- Cortical (cortical surface branches)
B
Branches:
NB superficial and deep
M1
Lateral lenticulostriate A. (NB ACA is the more medial vessel)
M2 (NB superior and inferior divisions)
Branches supply temporal lobe and insular cortex, parietal lobe, inferolateral frontal lobe via:
Superior:
Lateral frontobasal A.
Prefrontal sulcas A.
Pre-Rolandic (Precentral) and Rolandic (central) sulcal A.
Inferior:
3 temporal branches (anterior, middle and posterior)
Branch to angular gyrus
2 parietal branches (anterior, posterior)
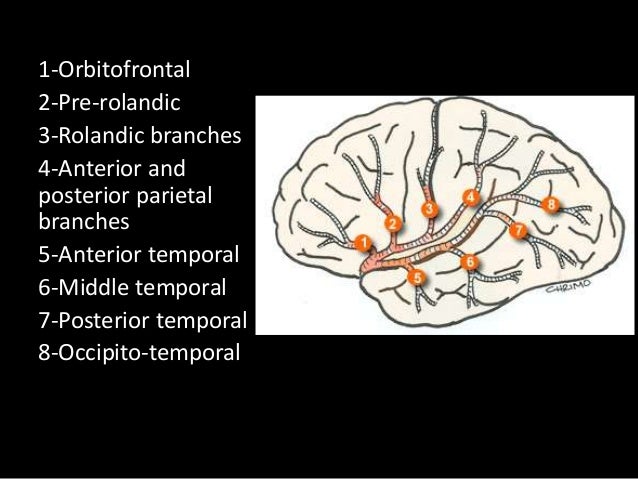
2-7 appear to be exclusively MCA branches. 1 shared with ACA. 8 PCA also.
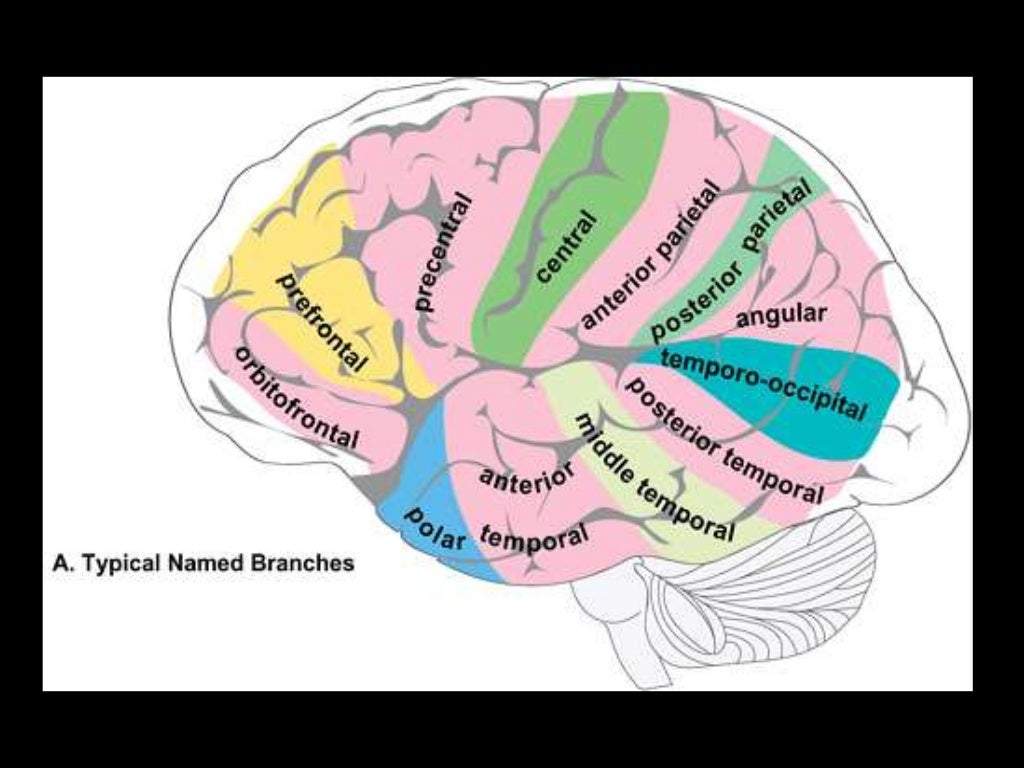
M3 and M3
The above branches will have M3 and M4 portions