Trigeminal Ganglion Balloon Rhizotomy Procedure
Background:
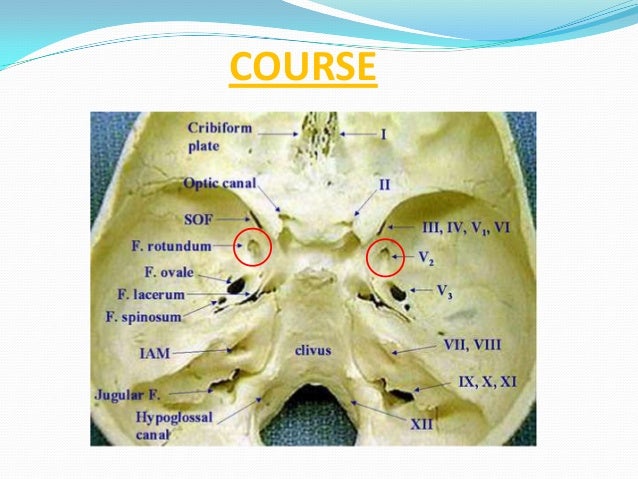
FO: foramen Ovale. TI Trigeminal impression (Meckel's gave is a dural recess which resides within this along the petrous apex).
Position: Supine, neck hyper-extended (20 degrees) and rotated 20 degrees to contralateral side. Gel roll seldom necessary.
Modified submental XR (draw trajectory vectors 2.5cm in front of tragus at inferior border of zygoma and mid pupilary line. Connect vectors to incision mark. Vectors also guide XR direction though there is a radiographers protocol)
Entry Point: c. 3cm lateral to mouth
Ensure no penetration into mouth (double gloves)
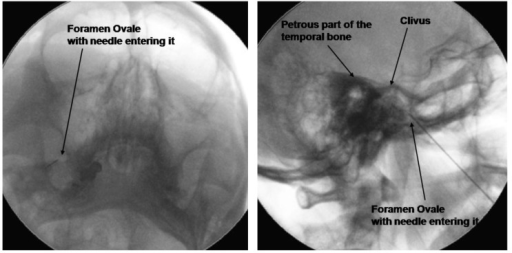
Trajectory/Target: Aim for middle of FO
Will feel give on puncturing foramen ovale and should see CSF in primary cases. Caution- too lateral may enter temporal lobe and too medial lacerum (carotid). Don't plunge too deep either- just penetrate.
Can also identify petrous bone on submentatal XR (key XR landmarks are mandible, maxillary sinus, zygoma and petrous ridge).
Once in, switch to lateral view.
Inflate balloon slowly with approximately 0.8mls of dye. Radiograph should look pear shaped (by 0.5-0.7mls) and bradycardia expected. Don't inflate more than 0.8mls or ballon will burst.
Dumbbell also acceptable, but sphere or irregular not (deflate and reposition).
NB distance from needle tip to mid balloon 14-17mm (use a steristrip as a safety guard).
A is incorrect (too high- up against sellar floor) B is correct and pear shaped.
1 and 6 pear shapes, 4 dumbbell. Others unacceptable.
Complication avoidance:
Diplopia most likely if balloon is too cranial (up towards sellar floor) or outside Meckel's cave (not pear shaped).
Regional anatomy: coronal section